Operating Systems
| Ιστότοπος: | ΕΛ/ΛΑΚ Moodle |
| Μάθημα: | Basic ICT Skills |
| Βιβλίο: | Operating Systems |
| Εκτυπώθηκε από: | Guest user |
| Ημερομηνία: | Τετάρτη, 4 Μαρτίου 2026, 1:09 AM |
Περιγραφή
An operating system is the most important software that runs on a computer. It manages the computer's memory and processes, as well as all of its software and hardware. It also allows you to communicate with the computer without knowing how to speak the computer's language. Without an operating system, a computer is useless.
1. What is an operating system?
2. The operating system's job
Your computer's operating system (OS) manages all of the software and hardware on
the computer. Most of the time, there are several different computer
programs running at the same time, and they all need to access your
computer's central processing unit (CPU), memory, and storage. The operating system coordinates all of this to make sure each program gets what it needs.
3. Types of operating systems
Operating systems usually come pre-loaded on any computer you buy. Most people use the operating system that comes with their computer, but it's possible to upgrade or even change operating systems. The three most common operating systems for personal computers are Microsoft Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux.
Modern operating systems use a graphical user interface, or GUI (pronounced gooey). A GUI lets you use your mouse to click icons, buttons, and menus, and everything is clearly displayed on the screen using a combination of graphics and text.
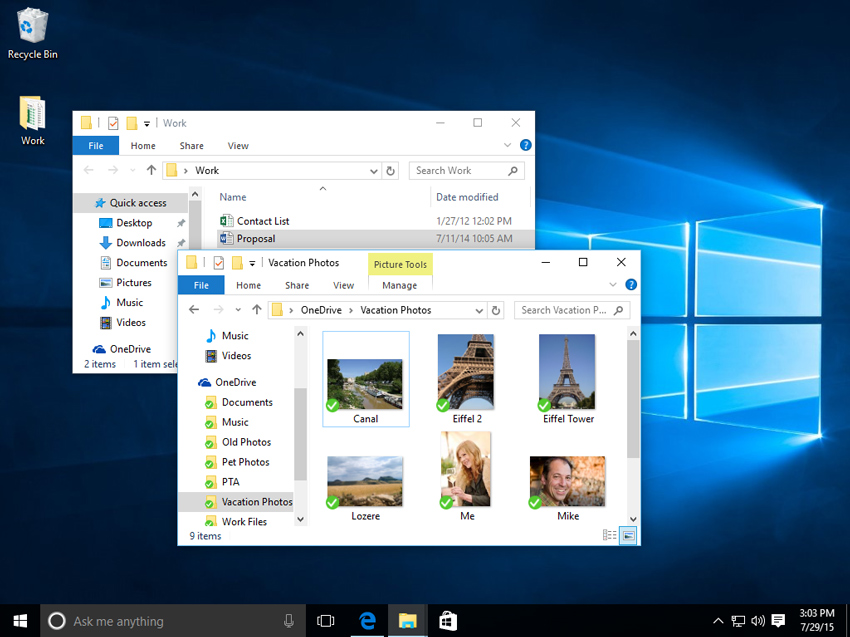
Each operating system's GUI has a different look and feel, so if you switch to a different operating system it may seem unfamiliar at first. However, modern operating systems are designed to be easy to use, and most of the basic principles are the same.
4. Linux
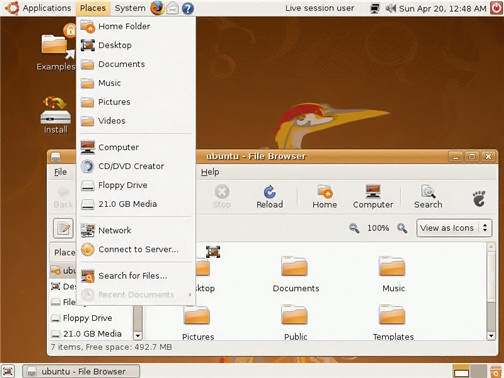
Linux (pronounced LINN-ux) is a family of open-source operating systems, which means they can be modified and distributed by anyone around the world. This is different from proprietary software like Windows, which can only be modified by the company that owns it. The advantages of Linux are that it is free, and there are many different distributions—or versions—you can choose from.
According to StatCounter Global Stats, Linux users account for less than 2% of global operating systems. However, most servers run Linux because it's relatively easy to customize.
5. Operating systems for mobile devices
The operating systems we've been talking about so far were designed to run on desktop and laptop computers. Mobile devices such as phones, tablet computers, and MP3 players are different from desktop and laptop computers, so they run operating systems that are designed specifically for mobile devices. Examples of mobile operating systems include Apple iOS and Google Android. In the screenshot below, you can see iOS running on an iPad.

Operating systems for mobile devices generally aren't as fully featured as those made for desktop and laptop computers, and they aren't able to run all of the same software. However, you can still do a lot of things with them, like watch movies, browse the Web, manage your calendar, and play games.